How to Buy Stocks and Shares
Tangible Bottleneck Technique
Author: Fadil Karim
Contact: insights@denarianalytics.com
17th June 2023
Updated: 3rd March 2024
How do AI Services Work?
An AI request, whether it be a ChatGPT prompt or Apples automated photo album creator, gets sent across the internet to computers in a data centre somewhere else in the world, allows the AI to create an output which gets sent back across the internet to your phone/computer.
The Current State of AI
AI has became a mainstream subject recently upon the release of OpenAI’s ChatGPT, a Natural Language Processing (NLP) AI service in January 2023.
Since then other Generative AI tools such as Midjourney’s Image Generation and D-ID’s Voice Cloning and Text-to-Speech services have added fuel to the AI fire.
To make things more interesting, Microsoft, the company that has control of OpenAI, is currently developing Copilot for Microsoft 365 (Microsoft Office), that allows users to use ChatGPT from within the software.
The increase in use of ChatGPT within software will further increase the computing demands of the service which will lead to OpenAI purchasing more computing power.
There are many AI startups and big corporations such as Apple, Alphabet (Google), Amazon, and Meta (Facebook) who are developing AI services and tools and all of them are also about to demand large amounts of computing power to train and run their AI services. Remember that many of these services are
People, whether they be the child who’s low-income parents can’t afford a private tutor, or the small business owner looking to cut costs so that he can compete with bigger businesses, will be using AI services to help them with their needs such as help with their homework or reducing the need for staff respectively.
All of this means that there is money to be made by investing in AI but the question is how can you invest to make the most money?
Warnings
Avoid focusing too much of specific AI companies. Yes they will make money, but many of them aren’t publicly listed and this includes OpenAI.
Avoid focusing on big companies that are developing and using AI services such as Apple, Google and Meta as their services will be used and their stocks will rise because of this but they are competing with each other and it is difficult to deduce who will win the most customers and which one will produce the highest percentage gains.
How to Invest with the AI Trend
The goal is to follow the supply chains until you find a companies that provides critical physical products at a bottleneck in one of the chains because that company is critical to the whole chain.
A chain’s range begins with the service at the top and ends at raw materials.
Step 1 - Break Down One Product and Identify Critical Points in the Chain
Let’s look at the Natural Language Processing service by OpenAI’s ChatGPT.
ChatGPT’s service requires use of a powerful computer, something that most people are not willing to purchase.
To get around this, OpenAI owns powerful computers that can run the ChatGPT software. User then send their text prompt to OpenAI who then use the ChatGPT software on their computer to process the user’s prompt and OpenAI then sends the output to the user.
This is currently how all AI services work.
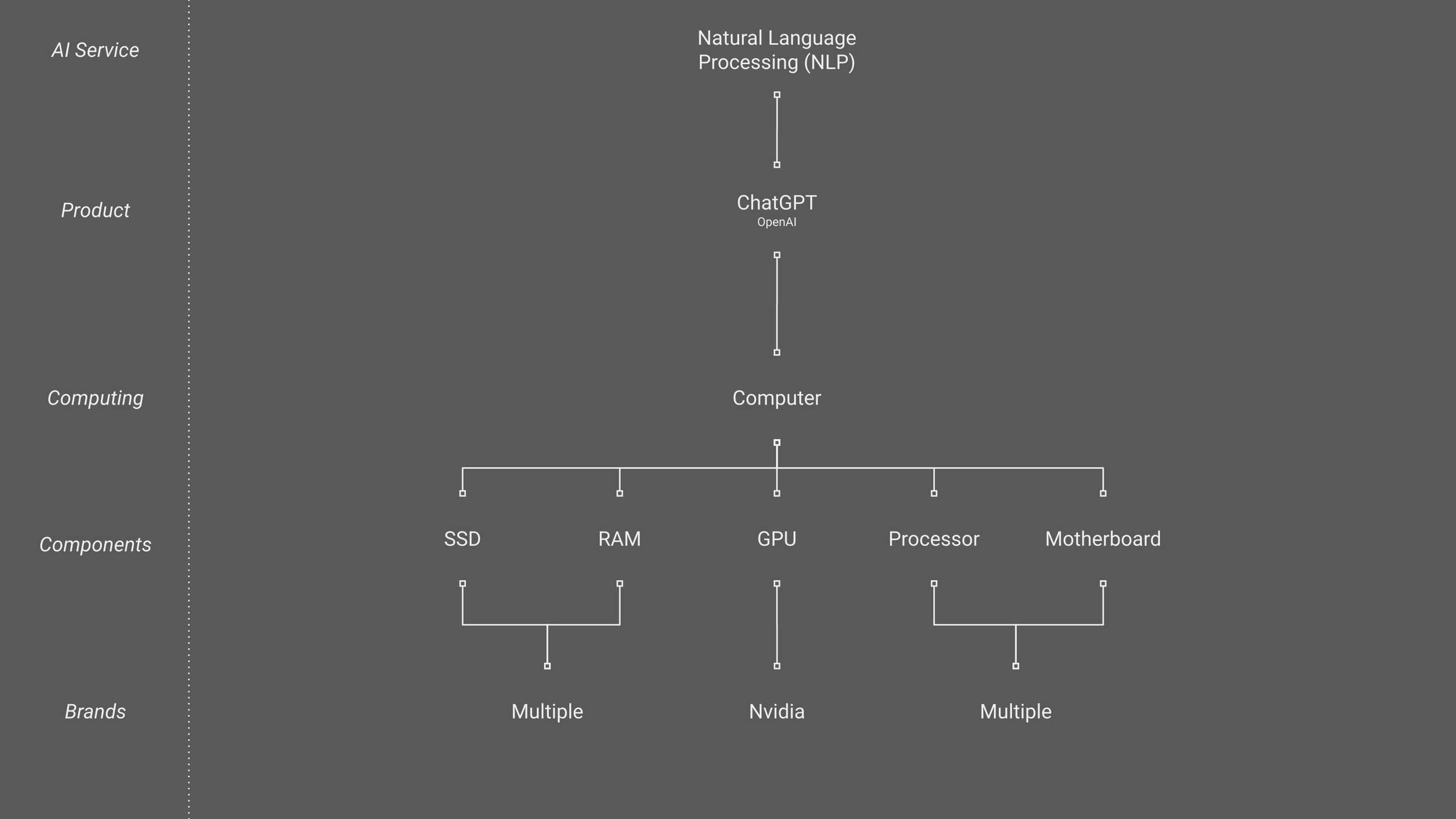
This means that ChatGPT and other AI services are heavily reliant on powerful AI-capable computers. AI-capable computers may be reliant on specific components, break down a computer into a list of its components then further break those down into their components. From here we can search for a bottleneck in the supply chain.
In the diagram below we can see that many of the components of a powerful computer can be supplied by multiple companies as no one company provides anything unique. For example, RAM memory chips can be supplied by many different manufacturers such as Crucial, Samsung, and others. This means that AI services, while reliant on this component, are not reliant on any specific company that sells them.
On the other hand, one of the components of a AI-capable computer, the GPU (AKA Graphics Card), is being supplied to the industry by one company, Nvidia. While competitors such as AMD exist, and new competitors, such as Google and Amazon are coming over the horizon, Nvidia is far ahead of all of these, hence, we have successfully identified a critical company in the AI supply chain.
But we must expand the chain further to see if there is more effective point on the chain to invest in and to see how reliant the AI industry is on the Nvidia GPU bottleneck so we can better decide if it is worth investing in.
Step 2 - Expand the Chain
Previously, we learned that a user of ChatGPT enters a prompt into the website which then gets emailed to OpenAI who run it through the ChatGPT AI on their local AI-capable computer, then emails the output back to the user who then sees it on their browser.
But this is only possible for a small number of customers. To become profitable, OpenAI needs hundreds of thousands of customers. This means that they need tens of thousands of these powerful computers, something that would cost too much for a startup.
This is where cloud services and the data centres which make them possible come in.
A cloud is effectively a large number of physical computers components stored in a large warehouse called a data centre.
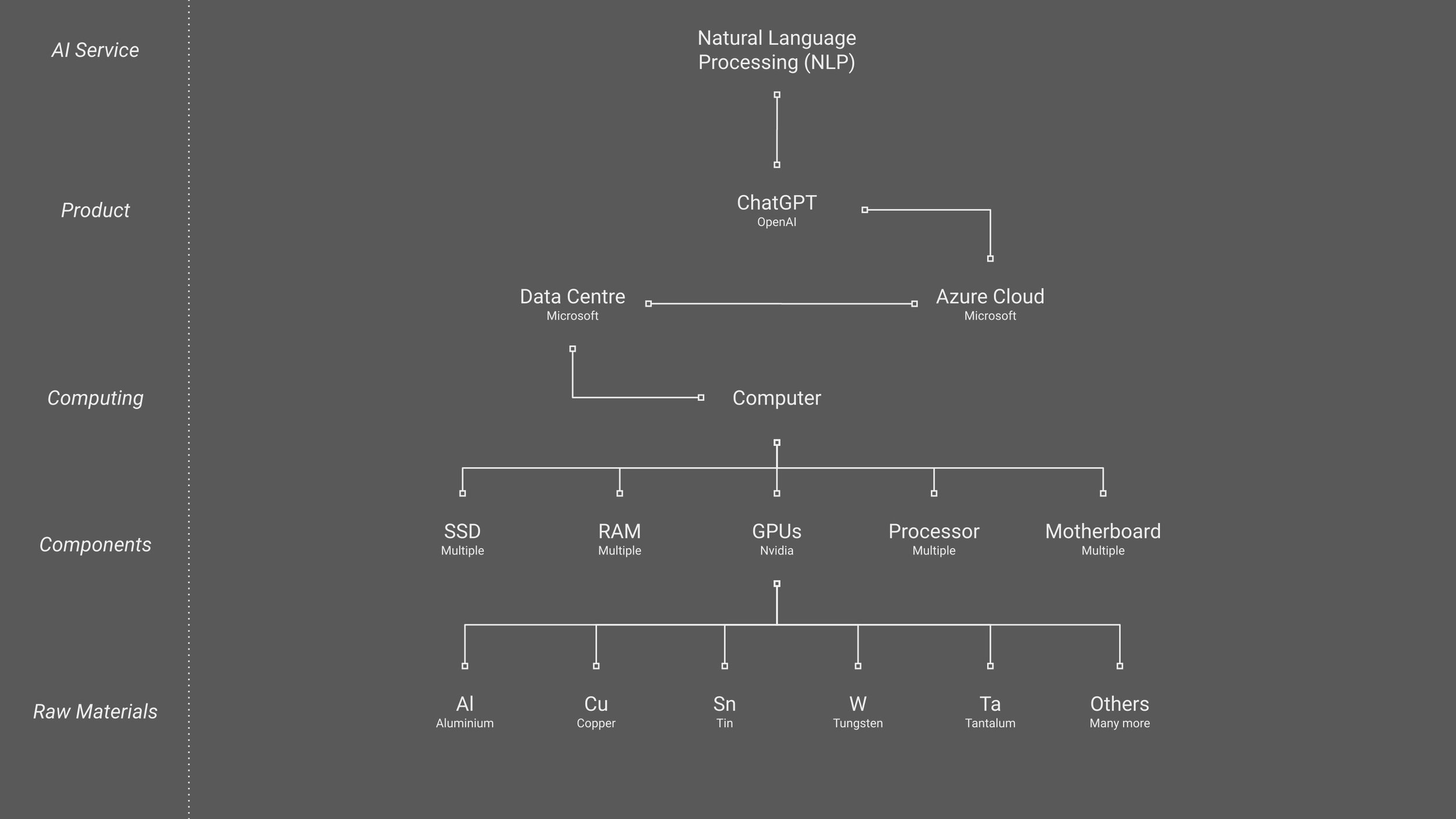
Microsoft runs a cloud service called Azure and OpenAI runs ChatGPT on this cloud. They rent use of the components by paying per minute/hour. As long as total subscription revenue surpasses the rental costs, ChatGPT is profitable for OpenAI.
In the diagram below, we have widened the chain to include the link between ChatGPT and AI-capable computing.
We have also broken down Nvidia GPUs into their raw materials to find additional bottlenecks. The same can be done for the other computer components and if there are any raw materials that is in low supply and high demand, it may be worth investing in these materials in the commodities market, or companies that extract and supply these materials in the stock market. For the latter, you would need to factorise the political risk and stability of the nation in which they operate in.
Step 3 - Expand Further
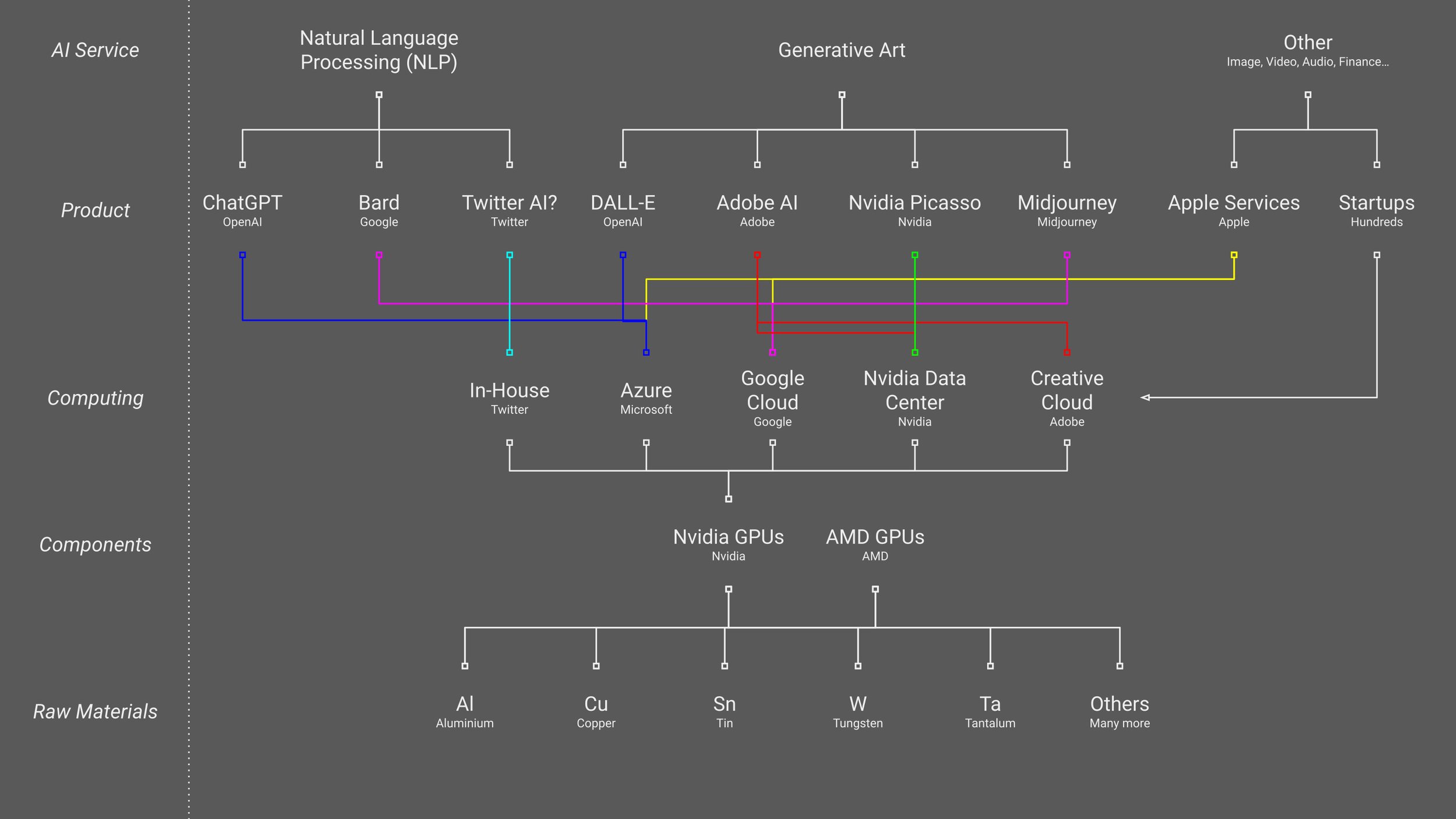
Expand the chain further to included competitors along the chain and their links. For example, Adobe AI rely heavily on Nvidia Data Centres.
We have removed non-GPU components from the chain for clarity and provided Nvidia’s closest competitor in that section.
Step 4 - Select a Critical Bottleneck
In this case, Nvidia sells tangible products that the entire sector depends on and they are miles ahead of the closest only competitor, AMD. Big companies that are established and sell tangible technology are good buys because their businesses are less scalable than software the other sectors such as AI services, hence it is more difficult for competitors to take sales from them meaning that an investment in this company is likely safer and more lucrative.